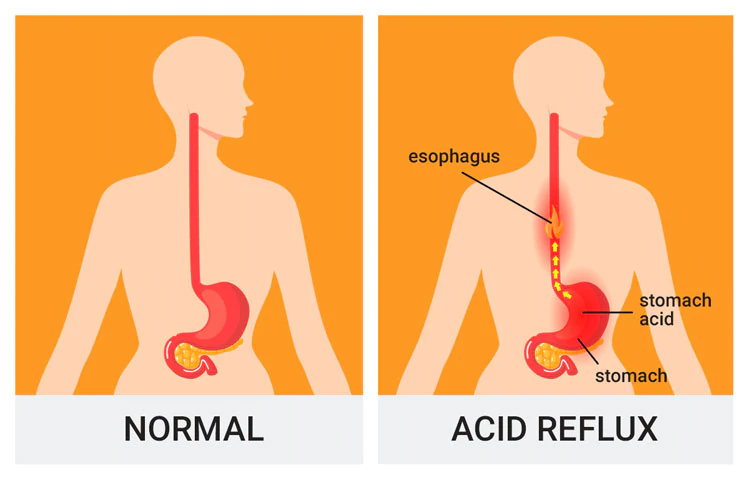
Acid Reflux Disease, also known as GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) or chronic acid reflux, is when acidic contents flow back into your mouth through your esophagus. In effect, causing heartburn, trouble swallowing, and acidic indigestion.
You may also feel like some food remains are caught up in your throat.
In fact, this happens when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) remains open after food is digested in the stomach.
LES is a circular band of muscle attached to the end of your esophagus. Notably, it relaxes and opens when you swallow, then tightens and closes again after swallowing.
Therefore, if your LES is not working properly or tight enough, it will cause an acidic reaction that causes your stomach’s contents to rise into your esophagus.
The acidic flow back into your throat will give you a sour taste. This condition is normal, and it happens to everyone.
When the symptoms persist for a long period, you develop GERD, as a result. Consequently, if left untreated, can sometimes cause serious complications.
Finally, the Salivary glands help produce saliva. This saliva contains bicarbonate which neutralizes the small number of acids left in the esophagus after swallowing.
What Causes Acid Reflux Disease?
The major cause of Acid Reflux Diseases is a common stomach abnormality called a hiatal hernia.
A hiatal hernia occurs when the muscle or upper part of your stomach moves above the diaphragm. Hence, exposing the diaphragm, which helps keep acid in the stomach.
Common symptoms of hiatal hernia are acid regurgitation and heartburn.
However, some other people can have acid reflux disease without heartburn. Instead, they have difficulty swallowing and experience hoarseness in the morning and chest pains.
Others may feel like choking, tight throat, bad breath, and dry cough.
What Is Heartburn?
To start with, heartburn is a burning sensation that flows from your stomach to the chest or abdomen.
The irritation causes the sensation in the esophagus lining caused by stomach acidity.
Ordinarily, the discomfort mostly occurs after eating or staying for long without grabbing a bite.
The condition worsens for some people. Especially, when they lie down immediately after eating, thus making it hard for them to get a nap.
Above all, this condition can be managed with acid indigestion drugs at the counter.
Besides, your doctor can also prescribe other forms of medication to manage and treat the condition.
How Is Acid Reflux Disease Diagnosed?
You will know it’s time to see your doctor when all your Acid Reflux symptom management programs are not bearing any fruit.
Some of the symptoms can be chronic and might not easily respond to over-the-counter medications.
Your visit to the doctor will make them run some tests on you to confirm a diagnosis and check for other problems. The tests are
Barium swallow (esophagram): This test checks for any ulcer symptoms or the narrowing of the esophagus. The doctor will allow you to swallow a solution to help structures show up on an X-ray during this test.
Esophageal Manometry: This test will check the movement and function of the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter.
pH monitoring: The test will be run to ascertain the acid level in your esophagus. Your doctor will insert a device into your esophagus and leave it for 1 to 2 days to measure the amount of acid in your esophagus.
Endoscopy scan: Endoscopy scan checks for any problem in your stomach or esophagus. The doctor inserts a long, flexible, lighted tube with a camera down your throat after spraying it with a sedative and anesthesia to make you more comfortable.
A Biopsymay Test: This test is taken during endoscopy under a microscope to check for tissues causing infection or abnormalities.
A Must-read- Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, Types & Treatment
How Common Is Acid Reflux Disease?
Acid reflux disease is prevalent, and it affects a huge number of people and is likely to affect anyone of any age. Some of the common causes of this disease are;
- Obesity or being overweight.
- Pregnancy
- Heavy smoking or being exposed to secondhand smoke.
- Some medications can also cause acid reflux
- What Foods Should I Avoid If I Have Acid Reflux?
First of all, you will need to change your eating habit and adjust your lifestyle and diet to manage acid reflux symptoms effectively.
Try and avoid these triggers that can cause a persistence of the symptoms.
- Fried foods.
- Spicy foods.
- Fatty (including dairy) foods.
- Garlic and onions.
- Tomato sauces.
- Alcohol
- coffee
- Carbonated drinks.
- Citrus fruits.
Many optional foods and drinks don’t trigger heartburn. A nutritionist can guide you on this and help you come up with a healthy diet.
Acid Reflux Disease Treatment Options
There are different measures that your doctor will ask you to put in place to manage and treat your acid reflux. These might include;
1. Making certain lifestyle changes
- Maintain a moderate weight
- Wait a few hours after eating to lie down
- Quit smoking
- Avoid big, heavy meals in the evening
- Elevate your head by 6-8 inches during sleep
2. Medication for Acid Reflux Disease
Your doctor can also prescribe medication or suggest taking over-the-counter (OTC) medications such as
· Antacids
These are used to calm mild symptoms of acid reflux and GERD. However, if you are used to taking them daily, you may need to see your doctor to suggest a stronger medication.
· H2 receptor blockers
The H2 receptor blockers reduce and manage the amount of acid your stomach makes. The medication is available over the counter for mild cases, and a doctor’s prescription buys stronger dosages.
· Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
This medication also balances the amount of acid your stomach makes. The inhibitor is stronger, and It works better than H2 blockers, especially when it comes to healing the esophageal lining, which has been torn by high acidity levels and overuse of antacids. You can also buy this medication Over the Counter, and your doctor can also prescribe you a higher dose.
· Foaming agents
Agents such as Gaviscon will be used to coat your stomach to prevent reflux.
· Prokinetics
Prokinetics such as Reglan and Urecholine can help reduce acid reflux, strengthen the LES, and empty your stomach faster.
Conclusion
All the above-listed medications have their side effects. Therefore, you need to take them cautiously and with your doctor’s recommendation.
Also, don’t use more than one type of medication at ago without your doctor’s guidance.